Multi-Functional Controllers (MFC)
What is a multi-functional controller?
Every free output of a Prozeda controller can be programmed with an additional function in a fast and easy way (also the free outputs of flex 400 when connected to grandis 650 HK). We call these additional functions Multi-Functional Controllers (MFR).
An MFR extends the pre-defined hydraulic layouts in a very flexible way.
Depending on a controller type there are up to 20 different multi-functional controller types available. The modular structure of this approach allows hundreds of combinations and can solve even very complicated tasks.
Multi-functional controller types:
- Temperature difference controller
- Heating
- Cooling
- Threshold value switch
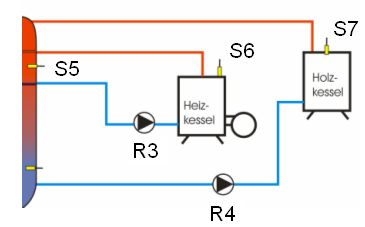
- Wood-fired boiler
- Return line boost
- Temperature range
- Circulation temperature-controlled
- Circulation time-controlled
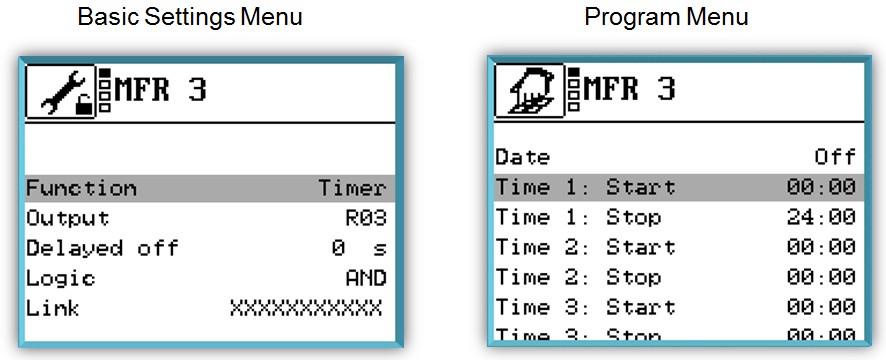
- Timer
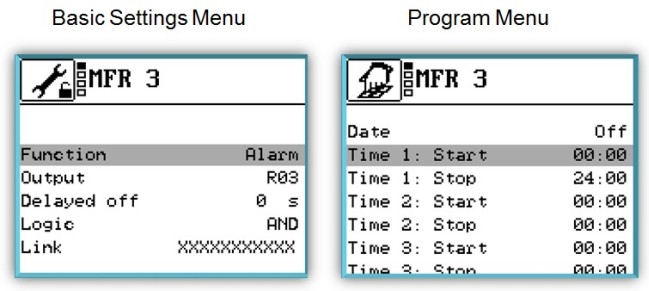
- Alarm
- HW reheating
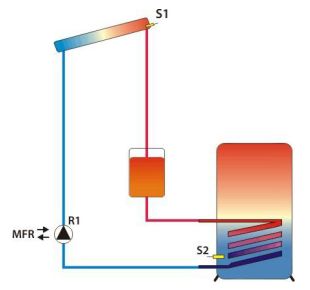
- Solar boost
- Solar redundancy
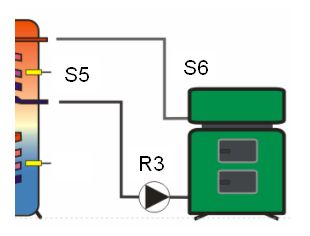
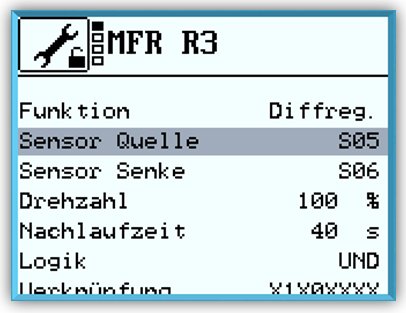
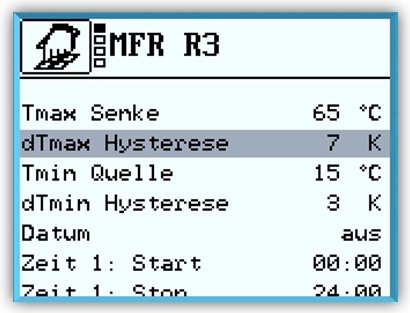
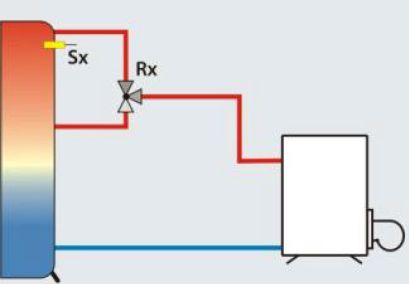
The Temperature difference controller is the most widely used function.
There is a measurement point at both the source and the sink. If the difference between the temperatures of the two measurement points exceeds a predefined value, the switching output of the multi-function controller switches on.
In addition, a minimum temperature can be set at the source and a maximum temperature at the sink. If the maximum temperature is exceeded or the temperature falls
below the minimum temperature, the switching output of the multi-function controller switches off.
Typical flow
- Funktion einschalten
- Parametrisieren
Examples
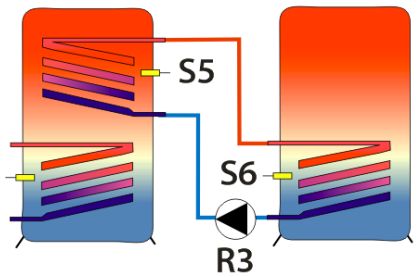
|
Reloading |
External heat exchanger |
|
Pool |
Pool with external heat exchanger |
Simple thermostat function. The switching output of the multi-function controller switches on as soon as the temperature falls below the preset switch-on temperature. If the temperature rises above the upper limit of the preset temperature range (hysteresis), the switching output of the multi-function controller switches off.
Typical flow
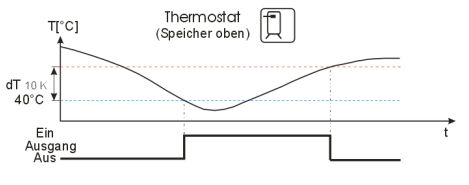
Example
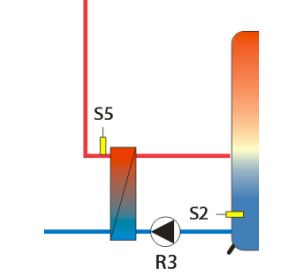
Re-heating
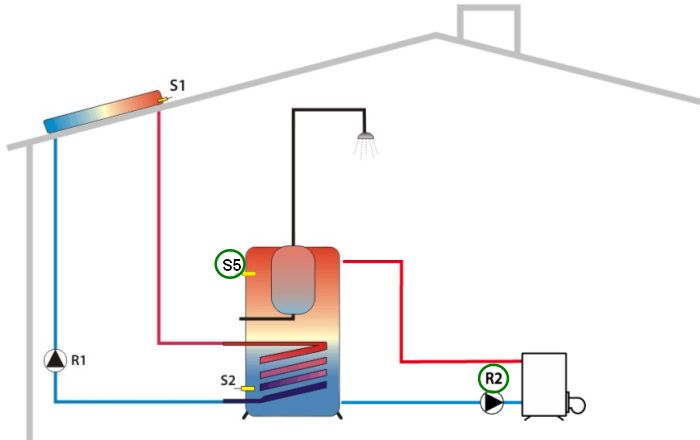
Output: R2, Source: S5
Simple thermostat function. The switching output of the multi-function controller switches on as soon as the preset switch-on temperature is exceeded. If the temperature drops below the lower limit of the preset temperature range (hysteresis), the switching output of the multi-function controller switches off.
Typical flow
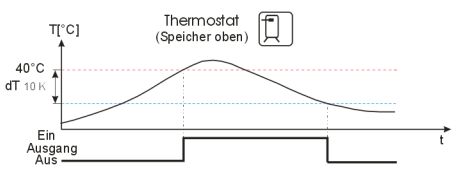
Example
Cooling
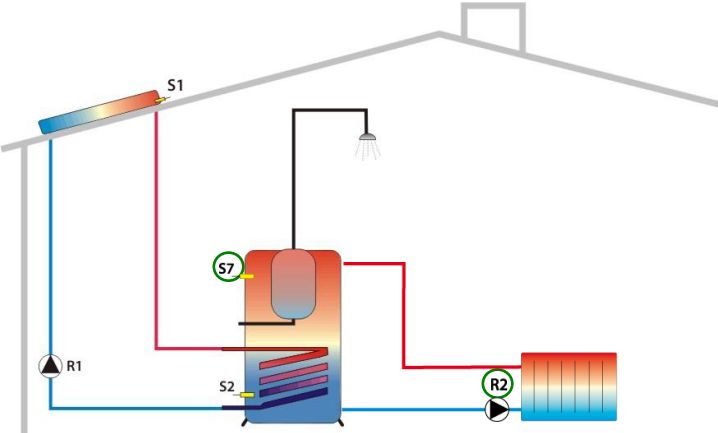
Output: R2, Source: S7
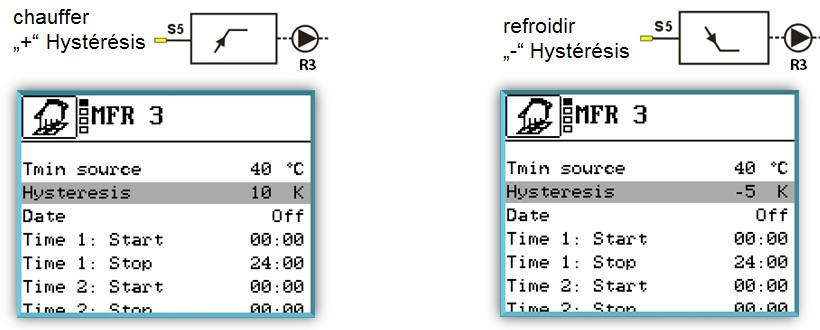
As a flexible option of the functions heating and cooling. the switching output of the multi-
function controller switches on as soon as the temperature reaches the preset switch-on
temperature. If the temperature drops below or rises above the preset temperature range
(hysteresis), the switching output of the multi-function controller switches off.
To use this function for heating, set the "Hysteresis" value to greater than 0. To use this
function for cooling, set the "Hysteresis" value to less than 0.
This function allows you to re-heat the storage tank from a solid fuel boiler. The switching
output of the multi-function controller will be activated if the boiler temperature (source
sensor) plus the selected temperature range (hysteresis) exceeds the storage tank
temperature (sink sensor).
In addition you can also define a switch-on temperature (setpoint temperature). In this
case the pump will not start until the switch-on temperature has been reached.
With this function the storage tank will be heated to a maximum temperature of 95 °C.
Examples
|
Tipical re-heating |
Two wood ovens |
To save energy, energy is supplied to the heating return flow from the solar circuit or storage tank. The mode of operation and relevant parameters are similar to those of the "Temperature difference controller" function.
Example
Return line boost
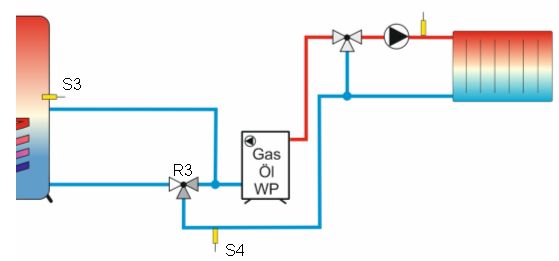
Output: R3, Source: S3, Sink: S4
With this function you can set the upper limit and the lower limit of a temperature range.
The multi-function controller will switch only within this temperature range.
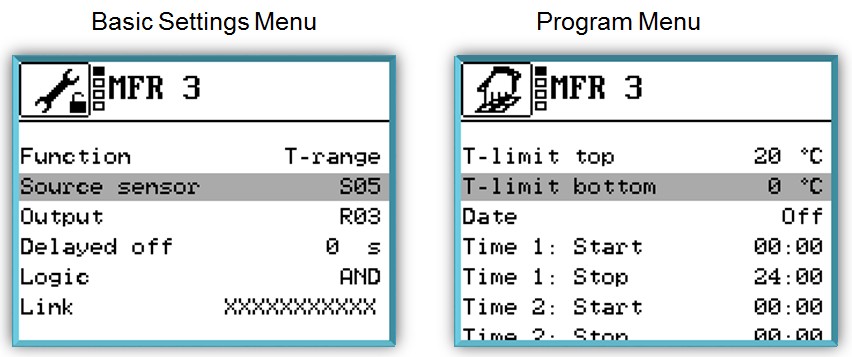
Output: R3, Sink: S5
The switching output of the multi-function controller switches on as soon as the temperature falls below the preset setpoint temperature. If the temperature rises above the upper limit of the preset temperature range (hysteresis), the switching output switches off.
Example
Temperature-controlled Circulation
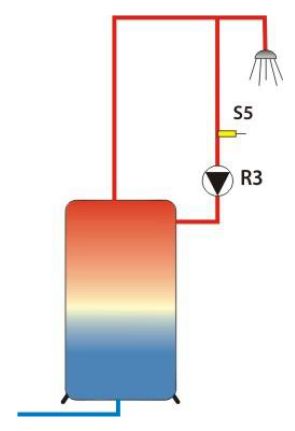
Output: R3, Sink: S5
The circulation pump is switched on and off in alternation within a preset time window. You can configure the setting for the duration of the respective runtime and waiting time.
Example
Time-controlled Circulation
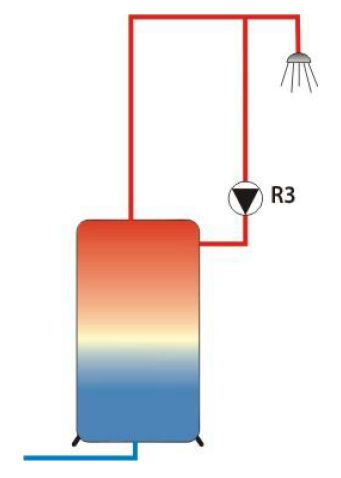
Output: R3
In the case of this function, the switching output of the multi-function controller switches
on within the preset time window. 3 time windows with runtime are possible.
Output: R2
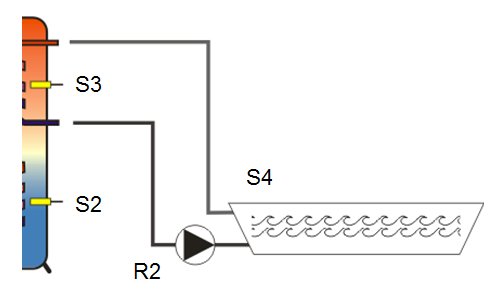
In the case of this function, the switching output of the multi-function controller switches
on or off when there is a fault on the sensors used. 3 time windows with runtime are possible.
Output: R3
With this function, the MFR output will be switched on when the hot water request is active. The HW reheating can thus be implemented in layers using a three-way reversing valve.
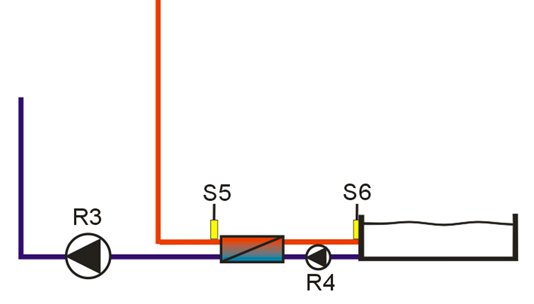
Example
Warm water re-heating
With this function, the switching output of the multi-function controller is linked either to the solar control or to the "drain-back" function. If the solar control or drain-back function is active, the MFC will be switched on, and at the end of the adjustable runtime it will be switched off again. If the solar control is switched off during this time, the MFR will also be switched off. For the MFC to react again when switched on, the solar power system must be continuously off for at least a selected off period.
Linking is possible to:
|
Solar control |
Drain-Back |
If a flow fault is reported during this function, the switching output of the MFC will be switched on and it will run in parallel with the solar power system. If the flow fault is rectified within the specified runtime, the link will be cancelled and the MFC will stop. If the flow fault still exists when the runtime has ended, the MFC will be permanently linked to the solar power system. This will be indicated by a fault message. You can use "Reset" to reset the permanent link to the solar power system. This will also reset the fault message.
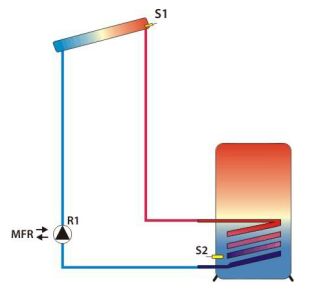
Solar redundancy
 |
|
 |
|